Breast Cancer – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Overview of Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women, and the second leading cause of cancer death in women after lung cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 1 in 8 women (about 12%) will develop breast cancer at some point during their lifetime.
There are several different types of breast cancer, which can differ in their prognosis and treatment. The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma, which begins in the milk ducts and accounts for about 80% of all breast cancers. Other types of breast cancer include lobular carcinoma, which begins in the milk-producing glands; inflammatory breast cancer, which causes the breast to become red, swollen, and warm; and Paget’s disease, which begins in the nipple.
Free Consultation
Get Breast cancer treatment cost estimate
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
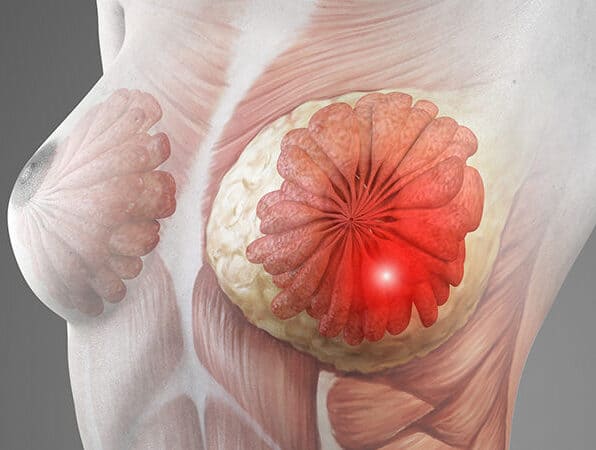
For each person, breast cancer symptoms might be different. Breast cancer may manifest itself in a variety of ways:
- The size, form, or contour of your breast has changed.
- A hard, painful lump that may be mistaken for a pea.
- A breast or underarm lump or thickening that persists throughout your menstrual cycle.
- A change in the appearance or feel of your breast or nipple (dimpled, puckered, scaly, or inflamed).
- Excess redness on your breast or nipple.
- The areola is a circular area that is distinct from any other region on either breast.
- This is a hardening or “marbling” of your skin, similar to marble.
- You may notice a clear or blood-stained milk discharge from your nipple.
Types of Breast Cancer
Angiosarcoma:
A lump or mass in the breast that may be accompanied by itching, redness, or pain. The lump may be visible on the skin or may be felt only during a self-exam or mammogram.
Ductal carcinoma in situ:
DCIS is a type of cancer that starts in the milk ducts. This cancer is non-invasive, meaning it has not spread outside of the milk ducts. It is considered an early stage breast cancer.
Inflammatory breast cancer:
An aggressive form that occurs in younger women. IBC is characterized by redness, warmth, and swelling of the breast due to the buildup of lymph fluid in the breast tissue.
Invasive lobular carcinoma:
It develops in the lobules of your breasts (where milk production takes place) and has eventually spread to surrounding tissues. It affects 10% to 15% of all breast cancers.
Lobular carcinoma in situ:
Precancerous condition where aberrant cells are present in the lobules of breast. It provides evidence that might indicate cancer later. Women with LCIS must have routine breast exam.
Male breast cancer:
A lump or thickening in the breast tissue, discharge from the nipple, or changes in the skin of breast. Men with these symptoms should see a doctor for further evaluation.
Paget's disease:
Paget’s disease of the breast is a condition where there is an overgrowth of the cells in the breast. It is more common in women who are postmenopausal.
Recurrent breast cancer:
Cancer that comes back after initial treatment. It can occur in the same place as the original cancer (local recurrence), or it may come back in another part of the body (distant recurrence).
Risks of Breast Cancer
A breast cancer risk factor is anything that raises your chances of developing breast cancer. However, having one or even a few of these factors does not necessarily indicate that you will develop breast cancer. Many individuals who get breast cancer have no known risk factors other than being women.
- Being female. Breast cancer is far more common among women than it is among men.
- Increasing age. Breast cancer incidence rises as you age.
- A personal history of breast conditions. If you’ve had a breast biopsy that reveals lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical hyperplasia of the breast, you have a higher chance of developing breast cancer.
- A personal history of breast cancer. If you’ve had breast cancer in one breast, you have a higher chance of getting it again in the other.
- A family history of breast cancer. Your risk of breast cancer increases if your mother, sister, or daughter was diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age. The majority of individuals who are diagnosed with breast cancer have no family history of the disease.
- Inherited genes that increase cancer risk. Because of the inheritance pattern, some hereditary changes that increase the likelihood of breast cancer can be passed from parent to child. The most well-known genetic mutations are BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genes raise your risk of breast cancer and other malignancies considerably; however, they do not guarantee that you will get cancer.
- Radiation exposure. If you received radiation treatments to your chest as a youngster or young adult, your risk of breast cancer is greater.
- Obesity. Obese individuals have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
- Beginning your period at a younger age. Your chance of getting breast cancer rises if you begin your period before the age of 12.
- Beginning menopause at an older age. You’re more likely to get breast cancer if you begin menopause later in life.
- Having your first child at an older age. After age 30, women who give birth to their first child have an increased chance of developing breast cancer.
- Having never been pregnant. Women who have never been pregnant have a significantly higher risk of developing breast cancer than women who have had one or more pregnancies.
- Postmenopausal hormone therapy. Breast cancer is more likely in women who use hormone therapy treatments that contain both estrogen and progesterone to manage the symptoms and signs of menopause. When women cease using these drugs, their risk of breast cancer declines.
- Drinking alcohol. Breast cancer is increased by drinking alcohol.
Prevention of Breast Cancer
- Check with your doctor about breast cancer screening. Discussing when to begin breast cancer screening tests and exams, such as clinical breast exams and mammograms, with your doctor is a good idea.
- Become familiar with your breasts through breast self-exam for breast awareness. Take the initiative to become familiar with your breasts by performing breast self-exam for breast awareness on a regular basis. Women may practice being aware of their breasts by examining them frequently while doing a breast self-exam for breast awareness. If there’s anything new in your breasts, such as lumps or other abnormal indications, contact your doctor right
- Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all. If you choose to drink, set a limit on the amount of alcohol you consume.
- Exercise most days of the week. Aim for 30 minutes of activity on most days of the week. If you haven’t exercised in a while, check with your doctor to see if it’s OK to start slowly.
- Limit postmenopausal hormone therapy. Hormone therapy may raise the risk of breast cancer. Discussions about hormone therapy’s advantages and risks should be had with your doctor.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If you maintain a healthy weight, focus on maintaining it. If you want to reduce weight, talk to your doctor about healthy techniques for doing so. Reduce the number of calories you consume each day and gradually increase the amount of exercise.
- Choose a healthy diet. Women who eat a Mediterranean diet rich in extra-virgin olive oil and mixed nuts may have a decreased risk of breast cancer. The Mediterranean diet is largely based on plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Instead of red meat, people who follow the Mediterranean diet consume beneficial fats like olive oil.
Our clinics are accessible from these cities

3000+
Happy Patients

1000+
Surgeries

10+
Doctors

Clinics Across India
Multi-
City
3+
Hospitals
Our Clinical Footprint
We provide easy storage and access to information from Mantra Care technology. Here, patients can easily acquire notes from virtual doctor consultation, treatment plans, prescriptions, and more from one place. Get medical information 24/7 from any digital device.
Mantra Care aims at creating a much more efficient experience for the patients through their cost-effective and quality-driven medical treatments.
We provide relatively lower cost treatments for almost every health problem making our company the best choice for patients. Mantra Care technology automates all the manual tasks for members and doctors, making it a viable choice for acquiring lower-cost treatments.