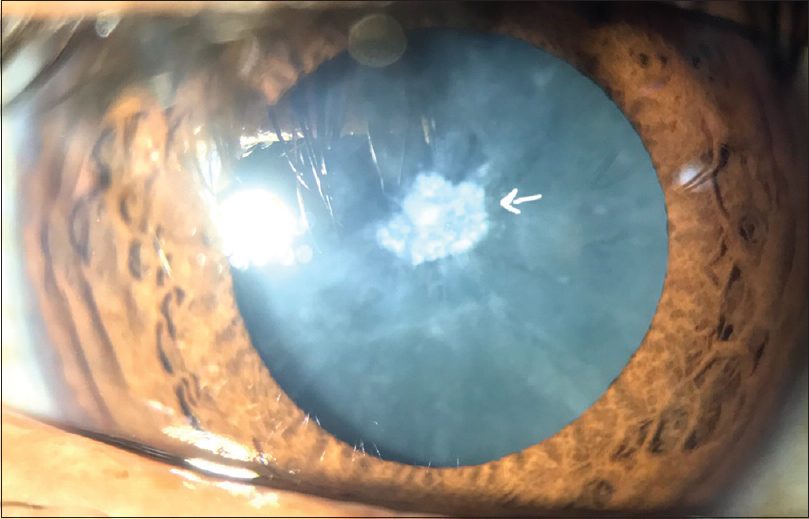
If you are a diabetic, there is a good chance that you will develop cataracts. Cataracts are a common complication of diabetes, and they can cause significant vision problems. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of diabetic cataracts. We will also provide tips for preventing them from developing in the first place.
Contents
- 1 What Is a Diabetic Cataract?
- 2 What Causes Diabetic Cataracts?
- 3 What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Cataracts?
- 4 How Cataract Is Diagnosed In Diabetes?
- 5 What Are The Treatment Options For Diabetic Cataracts?
- 6 The Connection Between Diabetes And Cataracts
- 7 What Are The Four stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy?
- 8 Can Diabetics regain eyesight?
- 9 Can Diabetic Eye Damaged be Reversed?
- 10 How Do Diabetics Keep Their Eyes Healthy?
- 11 Conclusion
What Is a Diabetic Cataract?
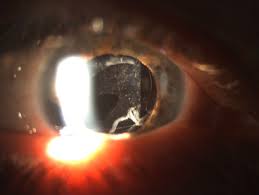
A Diabetic cataract is a type of cataract that develops in people with diabetes. Cataracts are cloudy areas in the lens of the eye, which can interfere with vision. In some cases, diabetic cataracts can develop rapidly and cause vision loss more quickly than normal age-related cataracts.
Diabetes is one of the most common causes for vision impairment. It has been reported that patients with diabetes are five times more likely to develop a cataract, especially when it happens early on in life. Thanks to the increasing prevalence of DM, the incidence of diabetic cataracts has also increased
What Causes Diabetic Cataracts?
High blood sugar levels are typically the cause of diabetic cataracts. When diabetes isn’t managed properly, glucose can build up in the lenses of the eyes and damage them, leading to the development of cataracts. High levels of glucose can also lead to an accumulation of protein in the lens, which increases the risk of developing cataracts.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Cataracts?
The most common symptom of diabetic cataracts is blurred vision. Other symptoms may include difficulty seeing at night, double vision, or sensitivity to light and glare. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your eye doctor right away to determine if you have diabetic cataracts.
How Cataract Is Diagnosed In Diabetes?
The diagnosis of diabetes is done through a physical examination and blood tests. During the physical exam, your doctor will check for signs of cataracts, such as cloudiness in the pupil or a yellowish tint to the lens. If your doctor suspects you have a diabetic cataract, they may recommend further testing. This could include an ophthalmoscope exam (to look at the back of your eye) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging (to create a detailed image of your retina).
What Are The Treatment Options For Diabetic Cataracts?

Diabetic cataracts are treated with surgery, typically in the form of a lens replacement or lens implant. During the procedure, your eye doctor will remove the cloudy areas from your lenses and replace them with new artificial lenses. This can help improve vision and reduce the risk of further damage to your eyes.
The treatment options for diabetes are as follows:
Surgery
One of the most common and effective treatments for diabetic cataracts is surgery. This involves removing the cloudy lens with a laser and replacing it with an artificial, intraocular lens (IOL). Surgery usually takes 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the procedure.
Intraocular Injections
Intraocular injections may be used to improve vision in a person with a diabetic cataract. The injection is typically made up of a steroid or anti-inflammatory medicine. These injections can reduce inflammation and swell in the eye, which often helps improve vision.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
PDT is a newer treatment for diabetic cataracts. It uses a laser to light up the cloudy lens and break it apart. The broken-up pieces of the lens can then be flushed away with eye drops or through surgery.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is another type of treatment for diabetic cataracts that can help improve vision. This involves using a laser to make tiny holes in the cloudy lens. This allows light to pass through the lens more clearly and reduces symptoms of diabetic cataracts.
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements
Several vitamins and minerals can help reduce the risk of developing diabetic cataracts, such as vitamin C, zinc, lutein, zeaxanthin, and omega-3 fatty acids. Taking supplements may help reduce inflammation in the eye and improve vision.
No matter what type of treatment you choose for diabetic cataracts, it is important to have regular checkups with your doctor so that any changes can be monitored and treated quickly. The best way to prevent the onset or progression of diabetic cataracts is to maintain healthy blood sugar levels through diet and exercise. Proper management of diabetes can reduce your risk for this condition and help preserve your vision.
If you think you may have diabetic cataracts, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible in order to prevent further vision loss. Your eye doctor can diagnose the condition and provide treatment options that are best suited to your needs. With early detection and treatment, it is possible to reduce the risk of vision loss and protect your eyes.
The Connection Between Diabetes And Cataracts
People with diabetes often contract cataracts and other eye problems, which can be a symptom of high blood sugar. To understand how blood sugar affects your body, it’s important to first know how high blood sugar impacts it.
Diabetes can cause dangerous levels of blood sugar, but fortunately, doctors have found a way to reduce the risk. If left unchecked, diabetes will slowly damage your eye vessels and cause eye conditions such as cataracts.
What Are The Four stages Of Diabetic Retinopathy?
The four stages of diabetic retinopathy include:
Mild Nonproliferative Retinopathy (MNR)
MNR is characterized by the presence of microaneurysms or small bulges in the capillaries (small blood vessels) in the back part of the eye. These can cause leakage of fluid and blood into other parts of the eye. Most people with type 2 diabetes have MNR at some point in their lives.
Moderate Nonproliferative Retinopathy (MNPR)
MNPR is characterized by the presence of more advanced microaneurysms and larger areas where the capillaries are blocked and not supplying blood to other parts of the eye. Some parts of the eye may start to swell as a result, and this can lead to vision problems.
Proliferative Retinopathy (PR)
PR is characterized by the growth of new blood vessels on the back surface of the eye. These new vessels are weak, so they can easily leak fluid into other parts of the eye. This can cause swelling and lead to vision problems.
Advanced Proliferative Retinopathy (APR)
APR is the most severe form of diabetic retinopathy and is characterized by very large areas of fluid leakage, scarring, and bleeding in the eye. This can cause permanent damage to vision if left untreated.
A diabetic cataract is a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy due to high blood sugar levels. This can lead to blurred vision, reduced night vision, and increased sensitivity to light. While this condition can occur in any type of diabetes, it is most common in people with type 1 diabetes or those with poorly managed type 2 diabetes. Treatment typically includes medications and/or surgery to remove the cataract.
In order to prevent diabetic cataracts, it is important for people with diabetes to keep their blood sugar levels under control through proper diet, exercise, and medication. Additionally, regular eye exams are recommended in order to detect any changes or signs of cataract development. If diabetic cataracts are detected, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible in order to prevent any further damage or vision loss.
Can Diabetics regain eyesight?
If your blood sugar levels change rapidly, the shape of your eye’s lens can be impacted and cause blurry vision. Fortunately, this effect is temporary and will cease once your blood sugar returns to normal levels. It is also possible to regain your vision with proper treatment.
In some cases, however, diabetes can lead to the permanent development of a condition called cataracts. Diabetic cataracts are one of the most common long-term complications of diabetes and can cause severe vision loss if left untreated.
Can Diabetic Eye Damaged be Reversed?
Unfortunately, damage caused by diabetic retinopathy is usually permanent. This disease isn’t reversible, but there are treatments available that may help improve your vision. These treatments won’t likely return your vision to what it once was, however, they can prevent your condition from worsening further.
How Do Diabetics Keep Their Eyes Healthy?
Diabetes can have an effect on the eyes, leading to a type of cataract called a diabetic cataract. It is important for diabetics to take steps to avoid developing this condition and keep their eye health in check.
The steps taken by a diabetic:
Maintain blood sugar levels
Keeping your blood glucose levels within the recommended range is key to avoiding diabetic cataracts. This can be done through a combination of diet, exercise and medications prescribed by your doctor.
Get regular eye exams
Eye exams are key for monitoring diabetes-related changes in the eyes and detecting any signs of diabetic cataracts. Diabetics should get their eyes checked regularly to make sure that their vision is not affected and that no changes are taking place in the eye lens.
Wear sunglasses
It is important for diabetics to protect their eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses. This can help avoid damage to the eyes and reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
Quit smoking
Smoking can increase the risk of developing diabetic cataracts, so it is important for diabetics to quit smoking if they are smokers.
Conclusion
It may be concluded that diabetic cataract is a condition in which the lens of the eye becomes clouded and partially or completely obscures vision. It is caused by long-term elevated levels of blood sugar, and it can be treated with laser surgery or intraocular lenses. Treatment is important as this condition can lead to significant vision loss if left untreated.
To help reduce the risk of developing this condition, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet, and keep blood sugar levels within the normal range. Additionally, regular eye exams can help detect any changes in vision before they become too severe. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments of diabetic cataracts, individuals can take steps to protect their sight.
Cataract surgery is a safe and painless procedure. At MantraCare we have a team of experienced eye surgeons, who will be happy to answer any questions on cataract surgery. Call us at +91-9711116605 for any inquiries.