Hip Replacement – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Overview of Hip Replacement
Hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the hip joint is replaced by a prosthetic implant. This operation is usually performed to relieve pain and disability in people with severe hip joint damage. Hip replacement surgery can be performed as a total hip replacement or a hemi (half) hip replacement.
In a total hip replacement, the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial materials. The ball-and-socket joint is replaced with a metal ball attached to a stem inserted into the femur (thighbone), and a plastic socket lined with metal or ceramic.
In a hemi hip replacement, only the ball portion of the joint is replaced. This type of surgery is usually performed on patients who have only minor damage to their hip joint.
Free Consultation
Get Hip Replacement treatment cost estimate
Why Hip Replacement?
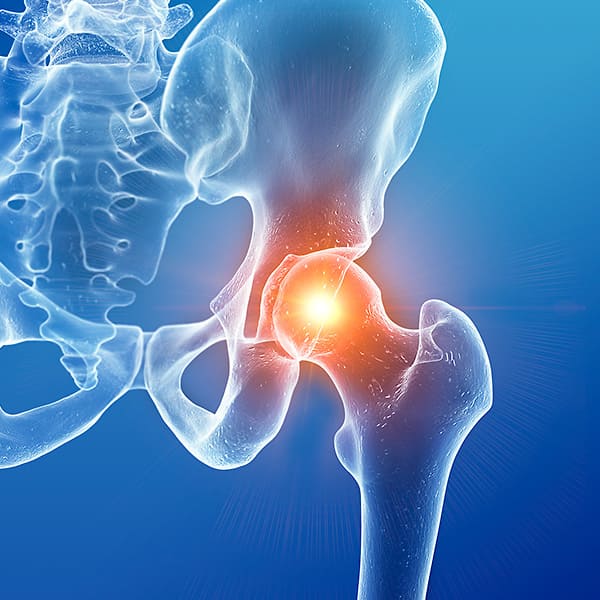
The following factors can put pressure on the hip joint and possibly necessitate hip replacement surgery:
- Osteoarthritis: Commonly known as wear-and-tear arthritis, attacks the slippery cartilage that covers the ends of bones and assists movement.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune disease in which the immune system becomes overactive, causing a form of inflammation that may erode cartilage and, in severe cases, underlying bone, resulting in damaged and deformed joints.
- Osteonecrosis: A bone might collapse and deform if there isn’t enough blood supplied to the ball portion of the hip joint, such as due to a dislocation or fracture.
- Posttraumatic arthritis: This can be the consequence of a significant hip injury or fracture. Over time, the cartilage may become damaged, causing discomfort and stiffness in the hip.
- Childhood hip disease: Even if hip difficulties are effectively handled in childhood, they may later cause arthritis. This occurs because the hip develops improperly, and the joint surfaces are damaged.
Types of Hip Replacement Sugeries
Total hip replacement:
It is usually done to relieve pain from arthritis or other hip problems. The surgery involves replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial (man-made) joint.
Partial hip replacement:
An option for people with arthritis in the hip. This surgery involves replacing only the damaged parts of the hip joint with artificial components, rather than the entire joint.
Hip resurfacing:
This involves placing a metal cap over the damaged ball of the hip joint and replacing the worn-out cartilage with a smooth, artificial surface. This preserves more of the patient’s natural bone and allows for a more rapid return to normal activities.
Risks After Hip Replacement
Risks associated with hip replacement surgery can include:
- Blood clots. After surgery, blood clots can develop in the leg veins. This is especially dangerous since a clot of material from the vessel might fracture and travel to the lung, heart, or very rarely, the brain. Blood-thinning medicines can help reduce this possibility.
- Infection. Deep tissue infections, including cellulitis and osteomyelitis, can occur at the surgical site and in the surrounding deeper tissue. Antibiotics are used to treat most infections, but a serious infection near the new hip might necessitate surgery to remove and replace the prosthetic components.
- Fracture. A fractured healthy chunk of the hip joint can occur during surgery. Sometimes the fractures are small enough to heal on their own, but larger fractures may require fixation with wires, screws, and/or a metal plate or bone grafts.
- Dislocation. In the early months following surgery, certain postures might cause the ball of the new joint to pop out of the socket, especially if they are done on a regular basis. A brace may assist in maintaining the hip in its proper position if it dislocates. Surgery may be required to stabilize an unstable hip.
- Change in leg length. Surgeons try to avoid the problem, but a new hip occasionally causes one leg to be longer or shorter than the other. Contractures of muscles surrounding the hip are sometimes responsible. In these situations, progressively strengthening and stretching those tissues may assist. After a few months, even modest variations in leg length aren’t usually apparent.
- Loosening. The new joint may not be firmly attached to the bone, or it might loosen over time, causing hip discomfort. To repair the problem, surgery may be required.
- Nerve damage. Occasionally, nerves in the region where the implant is put might be wounded. Nerve damage can result in numbness, weakness, and discomfort.
Recovery at Home after Hip Replacement
The modifications you make to your house during your rehabilitation may assist with daily chores. The following things might aid with normal activities:
- In your shower or bath, make sure there are securely fastened safety rails or handrails.
- Handrails along all stairwells should be secure.
- A comfortable chair with a sturdy seat cushion (that keeps your knees lower than your hips), a solid back, and two hands to assist in counterbalancing the strain on your upper body
- An elevated toilet seat
- A sturdy shower bench or chair for bathing is required.
- A long-handled sponge and a shower hose are essential.
- A dressing stick, a sock aid, and a long-handled shoehorn to help you put on and take off your shoes and socks without bending your new hip
- The upright-walking trolley holds your body in a completely neutral position. You may reach for objects without having to bend your hips much.
- Firm pillows for your chairs, sofas, and cars that allow you to sit with your knees lower than your hips
- Remove any loose carpets or electrical cords from the places where you walk in your house.
Our clinics are accessible from these cities

3000+
Happy Patients

1000+
Surgeries

10+
Doctors

Clinics Across India
Multi-
City
3+
Hospitals
Our Clinical Footprint
We provide easy storage and access to information from Mantra Care technology. Here, patients can easily acquire notes from virtual doctor consultation, treatment plans, prescriptions, and more from one place. Get medical information 24/7 from any digital device.
Mantra Care aims at creating a much more efficient experience for the patients through their cost-effective and quality-driven medical treatments.
We provide relatively lower cost treatments for almost every health problem making our company the best choice for patients. Mantra Care technology automates all the manual tasks for members and doctors, making it a viable choice for acquiring lower-cost treatments.