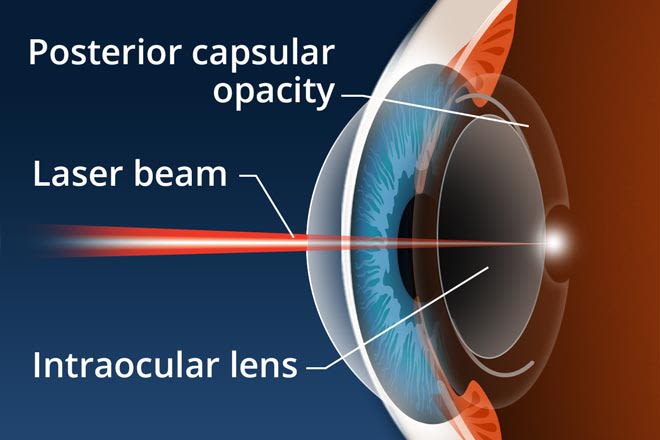
Cataracts are a common eye condition that affects millions of people all around the world. While there are many different types of cataracts, one of the most common is the capsular cataract. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for capsular cataracts.
Contents
What Is Capsular Cataract?
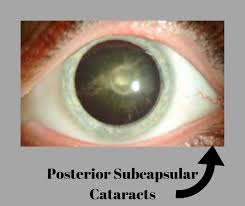
A posterior subcapsular cataract is a small, opaque area that forms near the back of the lens. This type of cataract often interferes with reading vision and causes problems seeing in both dim and bright light.
Posterior subcapsular cataracts (PSCs) are a type of cataract that typically occur in younger patients, usually in the cortical or nuclear layers. This type of cataract tends to be less common than other types of cataracts, such as cortical sclerotic or nuclear sclerotic. A posterior Subcapsular cataract is a type of translucent cataract that occurs when the back part of the lens gets full of a slippery medium. This can happen in either one location or many together, but the primary occurrence is mainly in combination with other types of cataracts. It causes significant loss of vision because it takes up the central region and there’s not enough room for light to reach your eyes.
What Are The Causes Of Capsular Cataracts?

To ensure a successful treatment process, it is important to know the various causes of our health condition. This can help lessen the problem as well as tell you how to prevent it in future. It’s also important that you know what each cause entails so that you can be prepared for any treatment process.There are various causes of capsular cataracts. They are as follows:
As we age, the proteins in our eyes can become disorganized and start to form a cloudy lens or “cataract” inside the eye’s capsule (the clear membrane that protects the lens). This is commonly known as an age-related cataract.
Diabetes
People who suffer from diabetes are at higher risk of developing a cataract. Diabetes can cause changes in the eye’s lens, making it more likely to form an opacity inside the capsule.
Eye trauma or injury
A severe eye injury can lead to a capsular cataract by causing enzymes and proteins in the lens to become disorganized and form a cloudy lens.
Long-term use of certain medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of developing a capsular cataract due to their effect on the proteins in the lens.
Genetic predisposition
Some people are predisposed to developing cataracts because of a genetic mutation that affects the proteins in the lens.
Radiation therapy
Prolonged exposure to radiation can damage the proteins in the lens and lead to a capsular cataract.
What Are The Symptoms Of Capsular Cataracts?
Many patients develop posterior subcapsular cataracts around the age of 40. It’s important to be alert for any symptoms as they can sometimes lead to complications. Some of the most common signs include pain, cloudiness, and floaters.
The most common symptom of capsular cataracts is blurry vision. In the early stages of cataract development, vision may be slightly blurred, and more difficult to focus. As the cataract progresses, it will cause more significant blurriness and eventually cause complete loss of sight if left untreated. Other symptoms of capsular cataracts include:
- Glare bright lights or sunshine can seem unusually bright or cause a “halo” effect around lights.
- Poor night vision and difficulty seeing in low-light conditions, such as at night or in dimly lit rooms.
- Fading or yellowing of colors: The colors may appear less vivid and washed out, with some shades appearing yellowish.
- Double vision: when the cataract affects both eyes, it can cause double vision.
How is Capsular Cataract Diagnosed?
You should have your eyes examined by a Professional if you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms: difficulty focusing, blurred vision at night, cloudy lens or vitreous, loss of color or contrast, floaters that are stationary or go away when looking away from them, new floaters or visible changes in the size. Or if you notice any other symptoms that your eye doctor suspects might be cataracts.
Slit-lamp examination is the best way to diagnose posterior subcapsular cataracts.
The ophthalmoscopic examination is also a good way for doctors to diagnose this condition, so it should be done as well. After an eye exam, follow your doctor’s advice about what treatment is best for you.
How Are Capsular Cataracts Treated?
A cataract is a condition that cannot be prevented no matter how advanced technology becomes. It can only be treated and cured through surgery. The classification and grading of cataracts are key factors to evaluating potential drugs because they are used to identify the severity of the disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) has simplified grading to encourage studies by ophthalmologists.
When a cataract is developing in the posterior subcapsular region, it generally develops a feathered appearance. When it is focused, the pupillary margin will be blurred and all the opacities will be made up of the retro illumination opacity only. The grading can be done according to vertical diameter. For multiple cataracts, you’ll want to consider only those most clearly visible cataracts with distinct borders when deciding where based on their score.
When it comes to treating capsular cataracts, there are a variety of treatments available, depending on the severity and type of cataract. Surgery is usually required for advanced cases where vision becomes impaired or severely affected.
There are various treatment options for capsular cataracts:
Surgery
This is the most common and effective method of treatment for capsular cataracts. During this procedure, a surgeon will make an incision in the eye, remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). The IOL is designed to restore vision to its pre-cataract levels.
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for patients with PSCC, as it can be used to address all four types of Phacoemulsification surgery. The procedure uses an Ultrasonic probe to break the cataract and suck the lens material out of the eye through a small incision (2-3mm). An IOL is implanted inside the eyes of patients that are in need of a lens replacement.
Medication
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help treat capsular cataracts. These include eye drops and/or oral medication which can help reduce the formation of new cataracts or slow down their progression.
Laser Surgery
Laser surgery may also be used to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an IOL. This method is generally considered less invasive than traditional surgery. Spectacles can help in some cases, but only to a certain extent.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy involves the use of a special light to treat cataracts and requires no incision in the eye, making it minimally invasive. However, this procedure is not recommended for treating advanced stages of capsular cataracts.
No matter which treatment option is chosen, it is important to remember that once a cataract has been treated, regular eye exams are still necessary in order to monitor for any recurrence or other vision problems.
If you believe that you may have a capsular cataract, consult with an eye care professional immediately. They will be able to identify the condition and suggest an appropriate course of treatment to help preserve your vision. Regular eye exams are also necessary to monitor for any recurrence of your condition as well as other vision problems. Taking these steps will help ensure that you maintain a clear, comfortable vision now and in the future.
Prevention Tips
There are various prevention tips :
1. Wear sunglasses that provide 100% UV protection to avoid ultraviolet radiation damage.
2. Cover your eyes with a wide-brimmed hat when in sunlight for long periods of time.
3. Have regular eye exams, especially if you are over 40 years old, as this is when the risk of developing cataracts increases.
4. Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as eating a nutritious diet and exercising regularly.
5. Don’t smoke or expose yourself to secondhand smoke, as smoking increases your risk of developing cataracts.
6. Avoid alcohol consumption and drink very sugary drinks like soda, which can cause diabetes and increase the risk for cataracts.
7. If you are taking any medications, talk to your doctor about their potential side effects and discuss ways to minimize them.
So these are the various prevention tips that are to be followed in order to reduce the risks of capsular cataracts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, capsular cataracts can be a serious condition that is often caused by aging or diseases. Symptoms may include blurred vision, increased sensitivity to light and glare, double vision and decreased color perception. Treatment options for capsular cataracts vary but are typically some combination of medications, laser therapy, photodynamic therapy, and/or surgery. It is important to speak with an ophthalmologist about the best treatment option for your particular situation. With early detection and timely treatment, capsular cataracts can be effectively managed to help maintain clear vision. Additionally, there are several prevention tips that can reduce the risk of capsular cataracts.
Cataract surgery is a safe and painless procedure. At MantraCare we have a team of experienced eye surgeons, who will be happy to answer any questions on cataract surgery. Call us at +91-9711116605 for any inquiries.