A coronary cataract is a rare form of cataract that affects the cornea. The cornea is the clear, dome-shaped part of the eye that covers the iris and pupil. In today’s technologically advanced world, there are many treatment options available for coronary cataracts. However, many people still suffer from the pain and discomfort associated with this condition without knowing what their options are. This article will break down what treatment options exist, and what factors you should consider before deciding how to proceed. Coronary cataracts can cause vision problems and may require surgery to correct them. In this blog post, we will discuss what coronary cataracts are, their symptoms, and how they are treated.
Contents
What Is a Coronary Cataract?
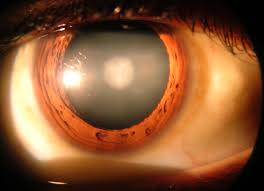
Coronary cataract, also known as snowflake cataract, is a type of congenital cataract that affects the back part of the lens in the eye. It is characterized by white and gray flecks distributed throughout the lens. This type of cataract can affect both eyes and usually appears between birth and age six.
Characterized by club-shaped and dot opacities distributed radially in the deep cortex, deep cortical neovascularisation describes a type of congenital cataract consisting of lens opacifications that may result in decreased vision. Upon further observation, this cataract characteristically encloses the nucleus in a seemingly crown-like configuration.
What Are the Symptoms of Coronary Cataracts?
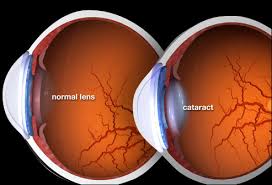
The most common symptom of coronary cataracts is decreased vision in one or both eyes. Other symptoms include light sensitivity, double vision, and a decrease in color perception. In some cases, cataracts can cause astigmatism, which causes blurred vision and distorted images.
Other signs that can indicate coronary cataracts include persistent headaches, dry eyes, eye strain, and the appearance of halos around lights at night. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor for further evaluation.
In advanced cases, a corneal scar or hazy area may form in the center of the cornea, leading to further vision loss. If this happens, you may experience difficulty driving at night or performing other activities that require sharp vision. In extreme cases, you may need corrective lenses or even surgery to improve your vision. It is important to get regular eye examinations so that any changes in vision can be caught early.
What Are The Causes Of Coronary Cataracts?
A coronary cataract is an opacity or clouding of the lens of the eye, commonly caused by a buildup of plaque.
Over time, this can cause the lens to become less transparent, which can lead to decreased vision and in some cases, blindness.
There are various factors that can contribute to the development of a coronary cataract, including age, genetics, and lifestyle habits.
Other factors that may contribute to the development of a coronary cataract include smoking, sun exposure, and alcohol consumption.
Some of the most common causes of coronary artery disease include hypertension, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, and obesity.
These conditions can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries leading to the heart, which in turn can cause the lens of the eye to become clouded. If left untreated, a coronary cataract can progress to blindness.
If you experience any signs or symptoms of coronary artery disease, please contact your doctor immediately for an assessment.
Risk Factors For Coronary Cataracts
There are a few risk factors for coronary cataracts, and knowing them can help you make an informed decision about your treatment.
Age
As you get older, your chances of developing a coronary cataract increase.
Race
Black people are more likely to develop coronary cataracts than white people. The reason isn’t clear, but it may be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Family history
If one of your parents has had a coronary cataract, you have a greater chance of developing one yourself. However, the risk is only about 50%.
Blood pressure
High blood pressure increases your risk of heart disease, including coronary heart disease. So getting your blood pressure under control can reduce your chances of developing a coronary cataract.
Cholesterol level
If you have this type of cholesterol you have: Higher levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) are associated with an increased risk of developing coronary heart disease, including coronary cataracts. So if you’re trying to lower your risk for heart disease, getting your cholesterol checked may be worth considering as part of the treatment for a cataract related to high cholesterol.
How Can You Diagnose A Coronary Cataract?
When you have a heart attack, the first thing your doctor will do is examine you and check for signs of injury. If they find any, they’ll refer you to a cardiologist. A coronary cataract is a type of heart attack, but it’s not always easy to diagnose on your own. That’s why it’s important to see a doctor if you experience any chest pain, shortness of breath, or sudden changes in vision.
There are different types of coronary cataracts, and each requires a different treatment plan. If you have a small-sized (less than 10mm) cataract, your doctor may opt to surgically remove it using laser surgery or a minimally invasive procedure called arthroscopy. If the cataract is larger or if there is another serious medical condition associated with it like diabetes or hypertension, then surgery may not be an option. In that case, your doctor may prescribe medication to reduce the size of the cataract or implant an intraocular lens (IOL) into your eye.
If you have symptoms that suggest you have a coronary cataract and don’t think you can manage them on your own, then it’s best to see a doctor as soon as possible.
What Are The Treatment Options?
There are three primary treatment options for coronary cataracts: surgery, laser surgery, and percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). Surgery is usually the most effective option and typically results in a high degree of visual rehabilitation. Laser surgery is less invasive but may not result in as high a degree of visual rehabilitation. PTCA is an alternative approach that uses balloon angioplasty to open up narrowed arteries in the heart. This may improve blood flow to the eyes and improve vision. There are also other treatment options available, such as pharmacological therapy and glasses with special lenses designed for people with cataracts. It is important to consult with an eye doctor about your specific situation before making any decisions about treatment.
There are various treatment options:
Surgery
Coronary cataracts can be treated surgically, but this is only recommended in cases where the cataracts are severely impacting vision. A surgical procedure called phacoemulsification can be used to remove the cloudy lens and then an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is inserted in its place.
Medication
Depending on the severity of the condition, medications can be prescribed to reduce inflammation in the eye or to slow down the progression of cataract formation.
Laser Therapy
In some cases, a laser procedure may be used to break up and remove cloudy areas of the lens that have not progressed too far.
Prevention
There are various prevention tips:
Wear sunglasses
Using a quality pair of sunglasses that provide 100% UV protection is the best way to protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays. This can help reduce the risk of developing cataracts in later life.
Eat healthily
Eating a balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, and other nutrient-rich foods can help improve overall eye health and reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
Exercise regularly
Regular physical activity can help strengthen your immune system, which can also help reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
Reduce alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of developing cataracts. Reducing or eliminating your alcohol consumption can help keep your eyes healthy.
Quit smoking
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing cataracts and other eye diseases. Quitting smoking is the best way to protect your eyes from harm.
Get regular eye exams
Seeing an ophthalmologist for regular eye exams is the best way to detect cataracts early. Early detection can help prevent more severe damage and vision loss in the future.
By following these prevention tips, you can help keep your eyes healthy and reduce the risk of developing cataracts in later life. If you are already suffering from cataracts, there are treatments that can help manage the condition and improve your vision. It is important to speak with an ophthalmologist if you think you may be suffering from cataracts. They can help diagnose the condition and recommend the best treatment options for you.
By taking proactive steps to improve your vision health, you can reduce the risk of developing cataracts and keep your eyes healthy and functioning correctly. Taking care of your eyes now can help ensure that
Conclusion
A coronary cataract is a condition that can cause vision impairment and other issues if not properly treated. It is characterized by cloudy areas in the lens of the eye and can be caused by various factors such as age, diabetes, or certain medications. Symptoms include blurred vision, difficulty seeing at night, and sensitivity to light. Treatment options include surgery, medications, and laser therapy. It is important to take steps to prevent cataracts from progressing and to seek medical advice as soon as possible if any symptoms are present. Early diagnosis and treatment can help preserve vision. Taking proactive steps to improve overall eye health can also help reduce the risk of developing cataracts in later life. With proper treatment, it is possible to manage coronary cataracts and maintain good vision.
Cataract surgery is a safe and painless procedure. At MantraCare we have a team of experienced eye surgeons, who will be happy to answer any questions on cataract surgery. Call us at +91-9711116605 for any inquiries.