There is a cataract in the eye that affects more than fifty million people worldwide. Punctate cataracts are the most common type of cataract, accounting for seventy percent of all cases. Punctate cataracts are caused by the gradual loss of lens material over time, which can result in a clouded or opacified lens. The cloudiness and opacity can interfere with vision, causing difficulty seeing close up and reading clearly. Punctate cataracts are often benign and do not require treatment, but they do require regular monitoring to ensure that the condition does not progress and worsen.
Contents
What is a Punctate Cataract?
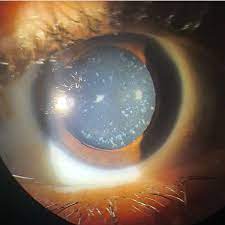
A punctate cataract is a type of cataract that has small, punctate spots in the lens. Punctate cataracts are most common in older adults and can be difficult to treat.
Punctate cataracts occur when the lens starts to become cloudy and granular (punctate). The spots are small enough that they can’t be seen with the naked eye, but they can be seen with an optical device such as a microscope.
The symptoms of a puncture Cataract may include vision problems, eye pain, and changes in how light reaches your eyes. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. In some cases, treatment for punctuate cataracts may involve surgery to remove the cloudy lens material.
The origin of a punctate cataract is unknown, but it seems to be more common in people who have had close contact lenses or eye surgery in the past.
Reasons For Punctate Cataracts
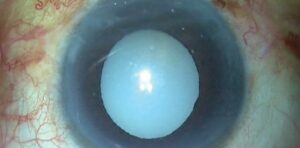
There are many reasons why a person might develop punctate cataracts, but the most common cause is age. As we age, our eyes lose elasticity, which can lead to the formation of small holes in the lens. These little tears in the lens allow light to scatter more than it would if there were no tears, and this results in decreased vision.
A punctate cataract is also commonly caused by complications from glaucoma or other eye diseases. If your eye has been inflamed for a long time, it may become very dry and swollen. This increased pressure can eventually damage the delicate cells in the eye that produce clear vision.
Another common cause of punctate cataracts is exposure to UV radiation from sunlight or indoor tanning lamps. Exposure to these harmful rays over some time can cause tiny lesions on the surface of the lens, which will eventually lead to punctate cataracts.
A final cause of punctate cataracts is age-related changes in the lens itself. As we age, the lens may become more brittle and less elastic, which can lead to the formation of small holes. The increased pressure from these tears in the lens can also lead to cataracts.
Some other causes can be an autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus in which the body produces antibodies that attack and destroy the optic nerve. In this condition, there may be intermittent episodes of blindness, during which the person can see fine points and lines but not overall shapes or scenes. The vision will eventually become completely impaired if untreated.
Symptoms of Punctate Cataract
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is likely that you have a punctate cataract. Note that not all sufferers will experience every symptom, and some may experience only a subset of them.
Fogging or misting up your vision when you look at a bright light.
One of the most common symptoms of a punctate cataract is that it causes your vision to become foggy or misty when you look at a bright light. This can be extremely frustrating, as it can make it difficult to drive, read, or even see your surroundings clearly.
Blurred or fuzzy vision.
Blurry and fuzzy vision is also common symptom of a punctate cataract. This can be especially bothersome, as it can make it difficult to see clearly even when you are not looking at a bright light.
A change in color vision.
Punctate cataracts can also cause a change in your color vision. This can make it difficult to distinguish different colors, which can lead to confusion and difficulty with day-to-day tasks.
Seeing stars or other bright lights.
Some people also experience seeing stars or other bright lights when they look at things. This can be incredibly disorienting and can make it difficult to see anything else in the world.
Difficulty seeing in low light conditions.
When you have a punctate cataract, it can be particularly difficult to see in low light conditions. This can make it difficult to drive or even read in dim light settings.
Sensitivity to bright sunlight and glare.
Also, people who have punctate cataracts may be particularly sensitive to bright sunlight and glare. This can make it difficult to see in direct sunlight, or when you are outside and facing off against the sun.
Constant fatigue.
Another common symptom of punctate cataracts is that people experience constant fatigue. This can make it difficult to get through the day and can lead to more serious issues down the line.
Making eye movements often cause pain.
Another common symptom of a punctate cataract is that it can cause pain when people make eye movements. This can make it difficult to read or do other tasks that require movement of the eyes.
How Does Punctate Cataract Impact Someone?

The impacts that one can have from a punctate cataract are varied and depend on the severity of the condition. For example, if a person has a small punctate cataract that does not cause vision problems, they may only experience some mild discomfort or eyestrain. However, if a person has a larger punctate cataract that blocks their vision significantly, they may experience significant discomfort and difficulty reading, working, or driving.
Additionally, people with punctate cataracts often have difficulty seeing in low light conditions, which can lead to decreased safety while walking or driving at night. These impacts of the condition can be crippling and severely limiting, necessitating the need for significant medical attention and care.
These impacts of a punctate cataract can be extremely frustrating and debilitating for people, and they often require significant medical attention and care to overcome. If you are experiencing significant difficulty seeing due to a punctate cataract, please seek help from a physician as soon as possible.
How to Diagnose Punctate Cataracts?
There are different ways to diagnose punctate cataracts. It is usually diagnosed by a doctor via an eye exam or a scan. The most common way to diagnose it is by looking at the inside of the eye with a microscope and seeing if there are any tiny spots or tears in the lens. Punctate cataracts can also be diagnosed by taking pictures of the inside of the eye using an ultrasound machine.
Some other diagnosis methods can be an MRI scan or a CT scan. Another way to diagnose it is by measuring the size and shape of the lenses. If the cataracts are large or if they are progressing, then other tests may be necessary, such as a lumbar puncture to measure the pressure inside the brain.
Also, Punctate cataracts can sometimes be a sign of other health problems, so it is important to consult with a doctor to determine if the cataracts are the only problem or if there are any other issues that should be checked out as well.
Doctors may also perform tests that will help determine the cause of punctate cataracts. These tests may include a biopsy of the lens to see if there is a specific type of cancer or an examination of the proteins in the eye to see if there is an autoimmune disease.
Treatment of Punctate Cataract

A punctate cataract is a type of cataract that has small, round, or knotty spots in the lens. Punctate cataracts are more common in people over 65 years old and can be caused by a number of factors. These are such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), environmental damage to the eye, and certain types of cancer. Punctate cataracts usually require surgery to remove the lens.
Treatment for punctate cataracts typically includes removing the lens and installing an artificial lens. Depending on the severity of the condition, other treatments may also be necessary, such as surgery to fix blood vessels behind the lens or medication to improve vision.
Some other treatment options can be surgically removing the blood vessels that feed the cataract. This will stop the growth of the cataract and may improve vision.
Another prevention option for cataracts is eating a balanced diet, getting enough rest, and avoiding smoking. Other prevention options are wearing sunscreen and eye protection, and getting regular eye exams. These also help identify and treat other potential health problems that can lead to vision problems.
Conclusion
A punctate cataract is a rare form of cataract that results from the accumulation of protein in the lens. This article provides an overview of the condition, as well as tips on how to treat it. If you or someone you know is suffering from punctate cataracts, be sure to seek out professional help. With early diagnosis and treatment, many people enjoy excellent vision with this type of cataract.
Cataract surgery is a safe and painless procedure. At MantraCare we have a team of experienced eye surgeons, who will be happy to answer any questions on cataract surgery. Call us at +91-9711116605 for any inquiries.